
There are two main steps to get started with the Vocoder in Ableton. We will see how you can use the Ableton Vocoder on vocals as well as drums. Vocoders can be used with many different sources but tend to sound the best with vocals. Retro filters can turn sounds narrower and louder.
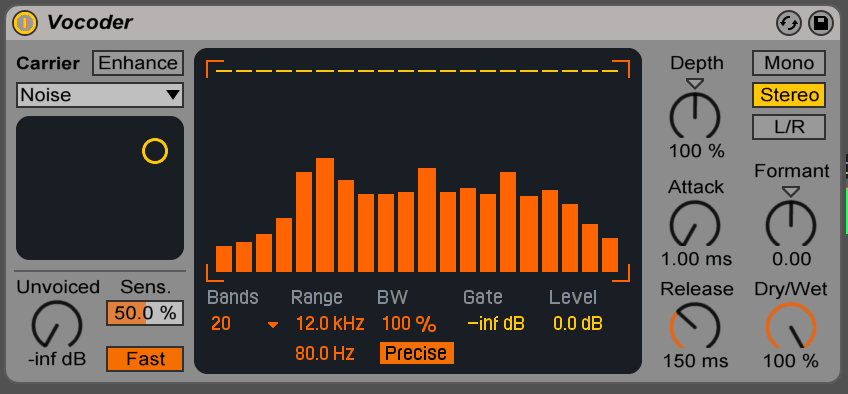
Setting the filter to “Precise” mode results in a wider bandwidth. Precise/Retro: The default vocoder from the Ableton live provides you with two filters Precise and Retro. 100% is usually applied to obtain the results of classical vocoding.Īttack and Release: These controls adjust how the vocoder reacts to the dynamics of the modulator signal. More bands means a more clear sound.ĭepth: This controls the amount of modulator amplitude envelope applied to our carrier signal. The sensitivity control next to this acts as a dry/wet for the carrier and the noise generator.īands: With bands, we can set the number of filters that can affect our sound.
VOCODER ABLETON LIVE DOWNLOAD GENERATOR
Unvoiced: This section deals with the volume of the noise generator and can also help with the brightness and clarity of the sound. The best thing about it is that all of this is done without changing the pitch of the signal. It gives the option to make a sound higher or deeper according to the taste. We can raise or lower the level of the bands in the drawing window.įormant: It is another great feature that will allow us to change the fundamental frequencies of our bands. This enhances the effect of the modulator envelope over the carrier source.įilter Bank: Tons of filters allow us to have complete control over the frequencies. Let’s explore the controls and parameters available with the vocoder.Įnhance: Located right next to the carrier selection, the enhance button will normalize the signal of the carrier across the frequency spectrum. The most common example for vocoder is a synth and a voice but you always have the option to experiment and feed different input to the modulator and carrier. The higher number of filters will yield the best possible results from the vocoder.

The number of filters corresponds with the quality of the result. Let us take an example, if a modulator gets a kick drum as an input, the lower frequencies of the carrier will be mapped onto it. The frequencies that are similar in the range are mapped together so that the original sound retains the base structure. The Filter Bankįilter banks are said to be the backbone of the vocoders where the sounds are split into different bands of frequencies. This produces the envelope for the carrier to follow. Each frequency band measures the dynamics of the modulator.
Think about it like a gate for the carrier.Ī modulators signal is split up into the frequency bands of the vocoder. The ModulatorĪ vocoder will analyze the dynamics of the modulator and use that signal as an envelope for the effect. This means that there is a pretty good amount of volume across the whole frequency spectrum. The CarrierĪ carrier signal is usually something that is harmonically rich. The modulator is used as an envelope source. The carrier is used to provide harmonic richness to the sound.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
